Websites are fantastic for showcasing your business or idea, but there’s a world beyond design and content. The online world has rules, just like the real one.
I’m not talking anything crazy, but there are some legal requirements for websites to make sure things are fair and safe for everyone.
Call it your website’s passport to legal compliance. These requirements not only keep you on the right side of the law but also enhance your website’s overall user experience.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be cruising smoothly and avoiding any unnecessary roadblocks that could hurt your website’s reputation and growth.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:Table of Contents
Imagine your website as your online storefront. You’ve got the products beautifully displayed, and the music’s just right, but have you thought about the legal signs you need to post up?
As a website owner, there are a few requirements that act like those signs, making sure your online space is safe, transparent, and operates according to the rules.

Here are key requirements that should keep your website safe and compliant:
Happy and informed visitors are more likely to return and engage with your website. And one way to ensure that is to show your website’s commitment to user privacy.
This is why a cornerstone of user trust is a clear and comprehensive privacy policy.
This document explains what information your website collects from visitors (think browsing habits or contact details), how it’s used (for targeted advertising or newsletter subscriptions?), and most importantly, how users can control their data.
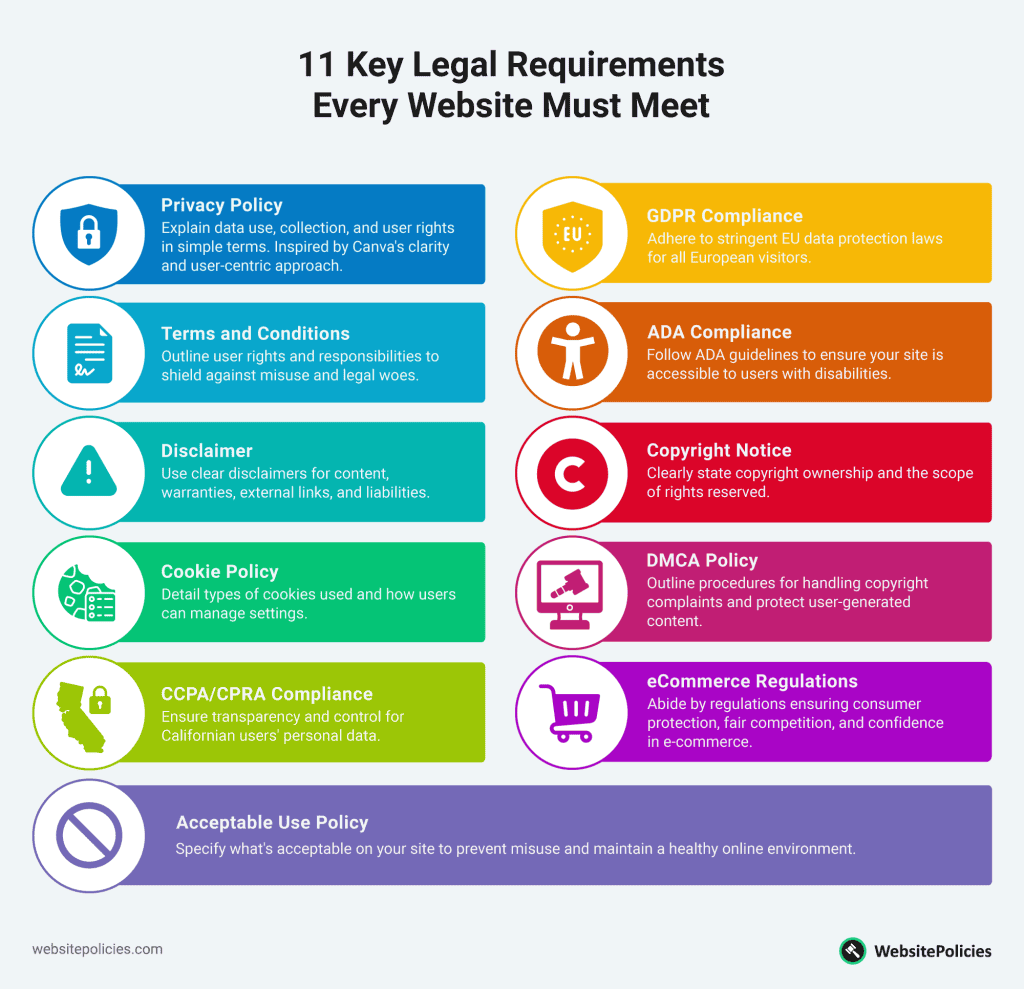
To show what a good privacy policy typically includes, let’s look at Canva’s Privacy Policy:
The example above clearly states what information Canva collects, going beyond just “personal information.” It also uses language that is easy to understand and shows it prioritizes user experience and the value of user data.
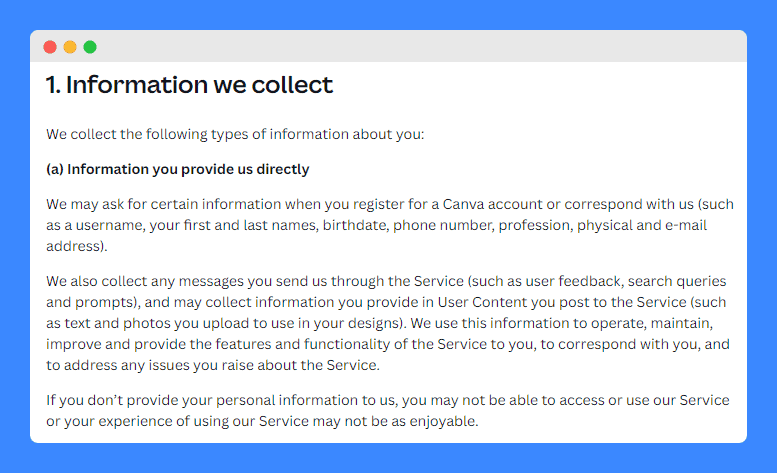
Here, Canva breaks down the use cases into clear categories. This makes it easier for users to understand the different purposes behind data collection. It also explains how it benefits the user.

To reduce any ambiguity, Canva states the reasons for sharing user information: providing the service, Canva’s legitimate interests, and with user consent.
Just like any well-run establishment, your website needs a set of rules to ensure a smooth and legal operation. This is where a Terms and Conditions page comes in.
Think of your website as a store or online space you’ve built. The Terms and Conditions act like a rulebook for visitors, outlining their rights and responsibilities while using your website. Here’s why it’s crucial:
PRO TIP: Place a link to your T&C in a prominent location, such as the footer, to make it accessible. For complex businesses, consult with a lawyer to ensure it is legally sound.
A disclaimer is a statement that clarifies your website’s limitations and protects you from legal responsibility. It informs users of what to expect from your content, services, or products.
There are various disclaimers you might consider for your website, depending on its content and purpose:



Cookies are small pieces of data that a website uses to store information about a user’s visit. While they may seem insignificant, they play a big role in how websites function and how they interact with users. That’s where a cookie policy comes in.
A Cookie Policy is a document that clearly explains how a website uses cookies and similar tracking technologies. It informs users about what types of cookies are used, why they’re used, and how users can control their cookie settings.
PRO TIP: Avoid technical jargon. The goal is for users to easily understand what information is being collected and how it’s used.
To comply with CCPA/CPRA, websites targeting Californians must prioritize user control over personal information. This means offering clear ways for users to:
Websites must also update their privacy policy to reflect these rights and explain how data is used. Investing in data security measures and obtaining user consent for data collection are also crucial aspects.
CCPA/CPRA compliance is an ongoing process. Staying informed about updates to the law and consulting with legal professionals can help ensure your website remains compliant.
Non-compliance can lead to significant fines (up to $7,500 per violation) and potential lawsuits from the California Attorney General or even consumers themselves.
Enforced by the European Union (EU) in 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict regulations on how the personal data of EU residents is collected, used, and protected.
While initially aimed at EU organizations, the GDPR’s reach extends to every website that processes the data of EU residents, regardless of the website’s location.
This means that if your website has visitors from the EU, understanding and complying with GDPR is essential. Here are some key steps to consider:
Websites have become essential tools for communication, information, and commerce. However, for users with disabilities, navigating websites with inaccessible features can create significant barriers.
This is where the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and its focus on web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG) come into play.
There’s no single solution for ADA compliance, as the specific requirements can vary depending on the website’s content and functionalities. However, here are some key steps to take:
In the digital age, where content is easily copied and shared, copyright notices act as a shield for your website’s creative assets.
A copyright notice is a simple but crucial legal statement that informs users about the ownership of the intellectual property on your website, typically text, images, videos, and other original works.
It should include:

If you want to allow others to use your content under certain conditions, you can explore Creative Commons licenses. These licenses provide a spectrum of permissions, allowing you to control how your work is shared and reused.
PRO TIP: While it serves as a deterrent and strengthens your legal position, it doesn’t guarantee complete protection. For solid copyright protection, consider registering your copyrights with the U.S. Copyright Office.
For websites that allow user-generated content (UGC) like forums, comment sections, or social media features, having a DMCA policy is not just a good practice, it’s a legal requirement.
The internet thrives on sharing information, but that freedom comes with a responsibility to respect intellectual property rights.
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a U.S. law that sets guidelines for online copyright protection and takedown procedures. To ensure DMCA compliance, check that the policy includes:
E-commerce regulations are a set of laws and guidelines established by governments or industry bodies to govern online business transactions. These regulations aim to:
These regulations are not meant to stifle innovation, but rather to create a fair and safe online marketplace for both businesses and consumers.
An Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) outlines the rules and expectations for how users can interact with your website. It discourages activities like spamming, hacking, or posting harmful content.
To ensure compliance, clearly display the AUP, educate users, and enforce the policy consistently. This protects your website from misuse and creates a positive online community.

Launching new websites opens doors to a global audience, but it also brings legal considerations. Here are some key website laws to be aware of, depending on your target audience and the nature of your business:
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a legal framework that regulates how the personal information of individuals in the European Union (EU) is collected, used, and protected. It’s considered one of the strictest data privacy laws in the world.
The GDPR sets high standards for data security, transparency, and user consent. Businesses must have a lawful basis for collecting data and be able to demonstrate compliance with the regulation.
Any organization processing the data of EU residents, regardless of the organization’s location, must comply with GDPR.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a landmark law that regulates how businesses collect, use, and share the personal information of California residents.
Websites that target California users or collect data from them must comply with these regulations to avoid hefty fines and potential lawsuits.
Enacted in 2018, this law establishes a baseline for data privacy rights in California. It empowers California residents with the following key rights:
The CPRA, California’s updated data privacy law enacted in 2023, requires websites to take user privacy a step further. It builds upon the CCPA and introduces several new provisions:
Designed to protect the privacy of young users online, the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) is a crucial law to consider if your website targets children under 13.
COPPA applies to websites that knowingly collect personal information from children. Here are its key aspects:
While CalOPPA (California Online Privacy Protection Act) might seem similar to the CPRA at first glance, it serves a distinct purpose.
Unlike the CPRA, which focuses on comprehensive data privacy rights, CalOPPA has a narrower scope. Its primary function is to ensure transparency around data collection practices.
Interestingly, CalOPPA applies to any website that collects personal information from Californians, regardless of the website’s location. This means if you have website visitors from California, you’d need to comply with CalOPPA’s disclosure requirements.
While the term “EU Cookie Law” is often used, it’s not entirely accurate. The relevant legislation is the ePrivacy Directive, which outlines regulations concerning electronic privacy in the European Union (EU).
A significant aspect of the ePrivacy Directive focuses on cookies and website tracking technologies. Here’s what you need to be aware of:
The ADA is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. While the ADA primarily applies to physical spaces, its reach extends to the digital world as well.
This means ensuring ADA website compliance is crucial to avoid discrimination and ensure your website can be accessed and used by everyone.
The ADA emphasizes equal access for all. It requires that websites be accessible to everyone, including users with visual impairments, hearing impairments, mobility impairments, and cognitive disabilities.
The CAN-SPAM Act (Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing Act) is a U.S. law that regulates commercial email messages, including those sent from a website.
A website may be subject to CAN-SPAM if it collects email addresses for marketing purposes. This includes signup forms for newsletters, promotional offers, or any email list where you plan to send commercial messages.
By adhering to CAN-SPAM regulations, you can ensure your email marketing practices are legitimate and avoid hefty fines for non-compliance.
Beyond these general legal considerations, there’s another layer of complexity to website regulations. Depending on the industry you operate in, there may be a specific list of legal requirements you need to address before you launch your website.
For websites in the healthcare industry, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) adds another layer of legal requirements.
HIPAA safeguards sensitive patient health information (PHI). They require that websites implement strict security measures to protect PHI, such as those allowing appointment booking, prescription refills, or access to medical records
HIPAA compliance involves securing data transmission, user access controls, and robust data encryption practices. Failing to comply with HIPAA can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage.
While the American Bar Association (ABA) doesn’t have the force of law, its ethical guidelines hold significant weight for attorney websites. These guidelines aim to protect consumers and ensure ethical advertising practices.
Following the ABA’s guidelines offers legal protection by reducing the risk of false advertising claims or disciplinary action from state bar associations. For attorney websites, adhering to these guidelines ensures professionalism.
In many areas, contractor websites need to consider state-specific licensing requirements. While there’s no federal law mandating it, many states require contractors to display their license ID on their business website.
This informs potential clients that you are a legitimate and qualified professional. Failing to do so could result in fines or even legal action.
PRO TIP: It’s always best to check with your state licensing board to confirm the specific requirements for contractor websites in your area.
Financial advisor websites are subject to regulations set forth by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
A key requirement is ensuring clear communication to avoid misleading investors. This means avoiding ambiguous language or exaggerated claims about investment performance.
Financial advisor websites should also disclose any relevant conflicts of interest and qualifications to ensure trust and transparency with potential clients.
Beyond the legal considerations, building a website involves several essential components that contribute to its overall success and user experience. Here are some key non-legal aspects to keep in mind:
The “About Us” section is a crucial element for building trust and transparency with your website visitors. It’s your chance to introduce your brand, its mission, and the team behind it.
Here, you can showcase your values, expertise, and what makes your business unique. A well-crafted “About Us” page can foster a connection with your audience and leave a lasting positive impression.
Providing clear and easy-to-find contact information is essential for establishing communication channels. This can include a phone number, email address, physical address (if applicable), and links to your social media profiles.
Making it easy for visitors to get in touch demonstrates your commitment to customer service and accessibility.
For an e-commerce website, a transparent and easily accessible Shipping, Return, and Refund Policy is important.
This policy clarifies customer expectations throughout the buying journey. It should outline shipping costs and timelines, return eligibility and procedures, and refund conditions.
A clear policy reduces purchase anxieties and helps manage customer service inquiries related to these areas.
Maintaining a positive online reputation is crucial. This means refraining from making false or misleading claims that could damage someone’s reputation, especially competitors or business partners.
Remember, defamation can lead to legal action, so it’s important to be truthful and objective in all your website content. If unsure about the accuracy of a statement, it’s best to err on the side of caution and omit it.
Yes, if your website collects any user data, a privacy policy explaining what data is collected and how it’s used is essential.
Follow WCAG guidelines to make your website accessible for users with disabilities, such as using alt text for images.
Yes, but CAN-SPAM regulations require user opt-in and clear unsubscribe mechanisms for commercial emails.
The CCPA requires clear user control over data. Offer options for users to access, delete, and opt out of data sales.
A well-crafted “About Us” section builds trust and connection by introducing your brand, mission, and the team behind it.